18.7Costs
The price is what you pay; the value is what you receive.Anonymous
Calculation of various costs involved in planning, implementing, and maintaining intelligent transport systems is a critical component for the transit agency. The BRT agency should estimate the probable capital and operating costs of the fare collection system during the planning stage, before the tendering process begins. Capital costs depend on the fare collection technology and the system scope—the number of buses, stations, depots, and terminals and expected passenger volumes. Keeping the system operational requires regular upgrades of software systems to update security and communication protocols. In addition, regular maintenance is required to ensure the proper functioning of fare gates and other hardware components.
Fare collection for BRT systems typically accounts for 7–12 percent of total operating costs, but has varied from 5 to 15 percent. In Bogotá’s TransMilenio, the fare collection operator receives between 7.56–9.1 percent of system revenue.
Table 18.4Fare and ITS costs (Phase I Project of 50 kilometers)
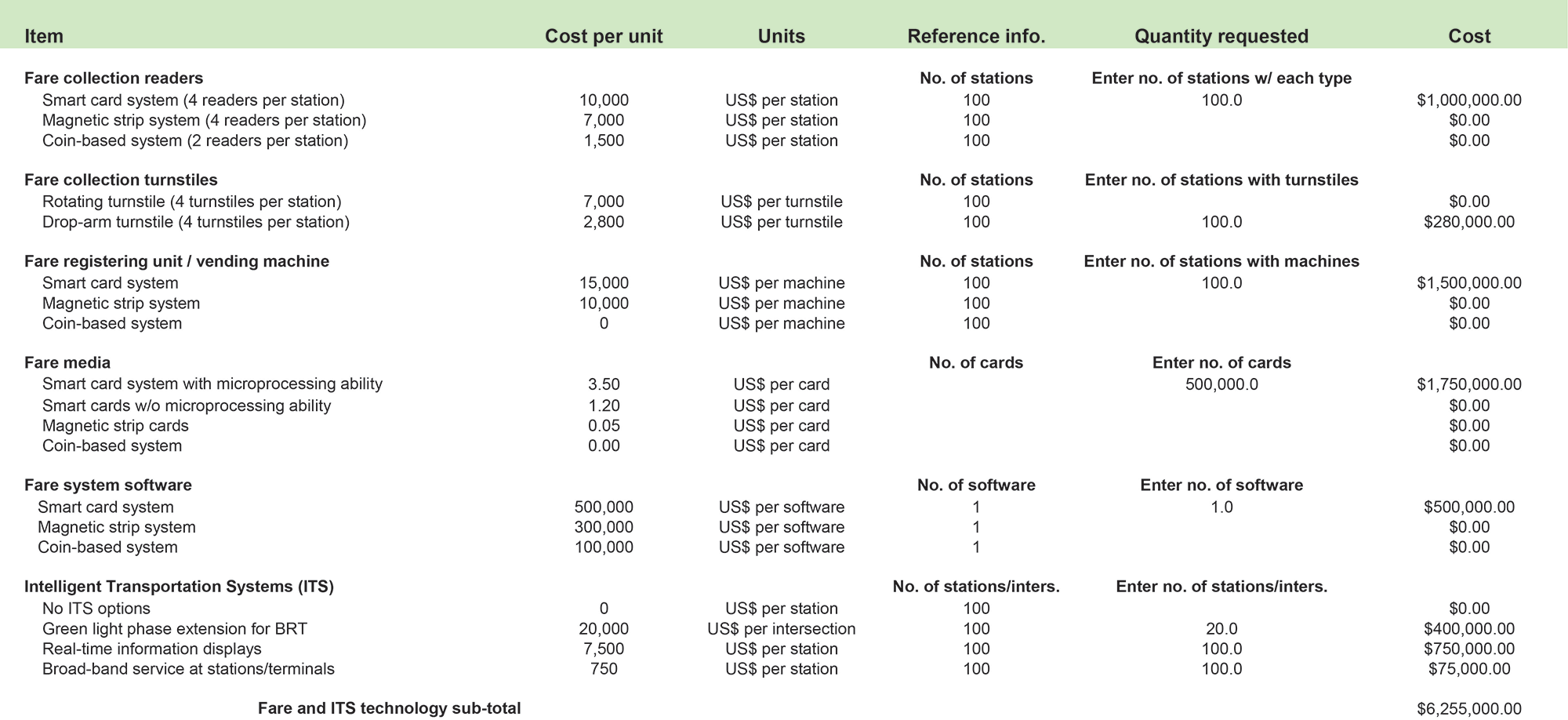
Table 18.5Capital Cost Components
| Fare Collection | Card validators; Ticket printers; POS (point of sales) machines; Computers; Access control barriers; Station servers; UPS; Communication network; Smart cards; |
|---|---|
| Control Center | Servers; UPS backup; Communications network; Bulk Initialization Machine (BIM); Printers; Computers; Biometric readers; Screens; |
| Software | Automatic vehicle location, fare collection, financial management, PIS, depot management, vehicle scheduling and dispatching, asset management and inventory, POS, BIM, card validators, web portal, servers, dashboard module, antivirus and cybersecurity, accounting, data transfer, data backup, report generation |
Table 18.6Operating cost components
| Manpower | Perks, benefits, salaries, fines |
|---|---|
| Transportation costs | Fuel, vehicles used by staff |
| Software | Upgrade and calibration, license and renewal fees, copyrights |
| Hardware | Regular equipment check, software calibration, life cycle analysis |
| Electricity | Power consumed by all hardware at stations, terminals, depots, interchange stations, transfer stations, central control center and administrative office |
| Communication costs | Telephone, mobile phones, and internet usage charges |
| Administrative costs | Stationery, printing, auditors’ fees, consultancy fees, advertisement and marketing, insurance, accident claims, legal matters, and other administrative work costs |
| Infrastructure costs | Maintenance, repairs, and rehabilitation works |
| Security | Stations, corridors, control center |
| Housekeeping | Cleaning of infrastructure (stations, terminals, depots) |
| Landscaping | Costs toward maintenance and planting of landscaping along corridor |